Learning Outcomes:
- List the basic components of a modern tractor
- Explain the basic operating principles of a tractor and identify common dangers associated with these
- Explain the preparation and maintenance requirements of tractors.
Pre-start Checks
Certain checks should be carried out each day before a tractor or other agricultural machine is started up and used. These check the basic systems of a tractor and include. Short via from Plumpton College showing basic checks for tractor with a plough attached.
Electric Tractors
With the current technology available for electric vehicles this is not practical for agricultural vehicles due to the weight and also the torque or pulling power needed. Should we need to move away from fossil fuels then it looks likely that we would keep an interna combustion engine using hydrogen as the fuel. JCB have been working on this for some time – this is a good video from Harry’s Farm about their progress.
Modern Transmission – John Deere.
These have come along way from when some of us first drove a tractor…

Preparing and using a tractor.
What must you do to prep tractor for job its doing?
What preps are needed for this….
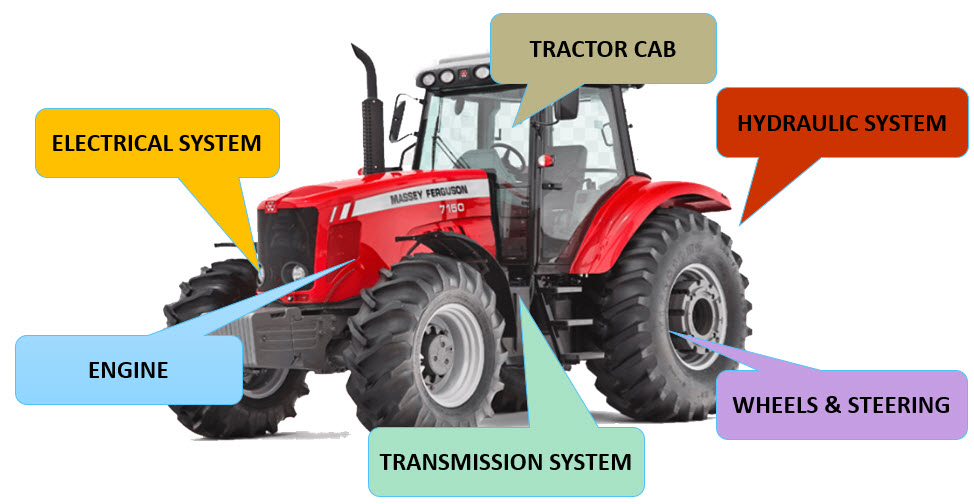
Basics of a tractor
The basic systems of a tractor …
Engines.
With few exceptions, farm tractors have a four-stroke, water-cooled diesel engine. Some older tractors have an air-cooled engine. Both types of engine are called internal combustion engines because fuel is burnt inside the cylinders to produce the necessary heat for them to work.
In contrast, a steam engine is an external combustion engine and the required heat is created outside the cylinder by burning coal or wood to produce steam which is directed into the cylinder.
Diesel engines are more robust than petrol engines as they have to withstand much higher working pressures and temperatures. They offer greater efficiency and economy compared with a similar size petrol engine and develop full power very quickly when started from cold.
Diesel engines are also known as compression ignition (CI) engines and petrol engines are sometimes called spark ignition engines.
Four Stroke Engine
Four-stroke engines have one working or ‘power’ stroke in every four strokes of each piston. Fuel (diesel) mixed with air sprayed into piston chamber. Temperature inside piston chamber causes ignition. High pressure and heat created at ignition of fuel.
3 of Pre-start Safety Checks
- Oil needed to lubricate movements
- Water need to cool engine block
- Air must be clean
- Unclean air = inefficient or no working
- Low oil or water = BANG!
Fuel System
The function of the diesel fuel system is to inject the correct quantity of clean, atomised fuel into the cylinders at the correct time in the four-stroke cycle. The components of a fuel system vary with different types of diesel engine. The amount of fuel injected will depend on the speed of the engine.
Air in the fuel can cause misfiring and in any quantity will stop the engine. Air will enter the fuel system if the engine runs out of fuel. The engine is unlikely to restart until the air has been bled (removed) from the fuel.
The lift pump Some engines have a lift pump, usually driven by the camshaft, which delivers fuel under slight pressure through the fuel filters to the injection pump. The lift pump may have a filter to trap any water and dirt present in the fuel and a hand-priming lever to bleed air from the fuel system. Fuel systems without a lift pump rely on gravity feed to the filters and the injection pump.
The fuel filter removes all traces of dirt from the fuel and some have a water trap to collect any water that may occur through condensation in the tractor fuel tank. Some engines have two fuel filters. Fuel filters must be renewed periodically usually after 600 hours or at the service indicated in the operator’s manual. A bleed screw on the filter unit is used to remove any air trapped in the fuel system after renewing the filter element or if the tractor runs out of fuel.
Electrical System
- Lights etc = 1 of Safety Checks
- Many functions now due to the in cab computers.
- The charging system provides most, if not all, of the electrical current needed when the engine is running at normal operating speed.
- The battery provides backup when the engine idles and the considerable amount of power required by the starter motor when starting the engine.
- When the engine is running the battery is charged by the alternator
Transmission System
- 2 of Pre-start Safety Checks
- Transmission + Hydraulic system = 1 in most tractors now
- Basically how the power gets from the engine to the wheels to drive the tractor along.
- Very complex now many are Vario drives no longer have to select a gear just accelerate or push a lever forward without even using a clutch….
- Other systems are:
- Hydraulic System
- Wheels and Steering
- Tractor Cab
Can you identify the Pre-start checks
Below is presentation which gives more details about “Machinery – Using Power : Tractor Workings”





