Learning Outcomes:
- Identify appropriate measures to control the risks in agriculture:
- Hierarchy of risk control measures
- To state the 2 key terms involved with a risk assessment
- To list the 5 steps involved with a risk assessment
- Complete own risk assessments
Even if you think you know
You actually do risk assessments all the time….
Have you ever stood at the side of a road, ready to cross and spotted a bus or lorry approaching at full speed and made the decision to wait until the vehicle had passed before crossing?
Well there you have it.
You’ve done a risk assessment.
No paperwork or rules and regulations to follow.
Hazard & Risk – Two Key Terms
Hazard
something that can cause harm…
…like a chemical
Risk
the chance that someone will be harmed…
low risk if the chemical is labelled and locked away…
…high risk if it is kept where a child can drink it
HAZARD:
A live LION is always a hazard. It always has the potential to cause you harm. SO a HAZARD is anything that can cause you HARM.
RISK:
A loose TIGER is a risk as it is likely it will cause harm to someone. In general a RISK is a combination of the severity of harm and the likelihood that harm will occur.
Risk Control.
Remove the hazard completely. Keep goldfish! If you cannot remove hazard? Avoid the hazard – do not go to the zoo!
Risk control measures. A TIGER is less of a risk if it is in a cage.
THUS
A cage is a RISK CONTROL MEASURE Or a PRECAUTION.
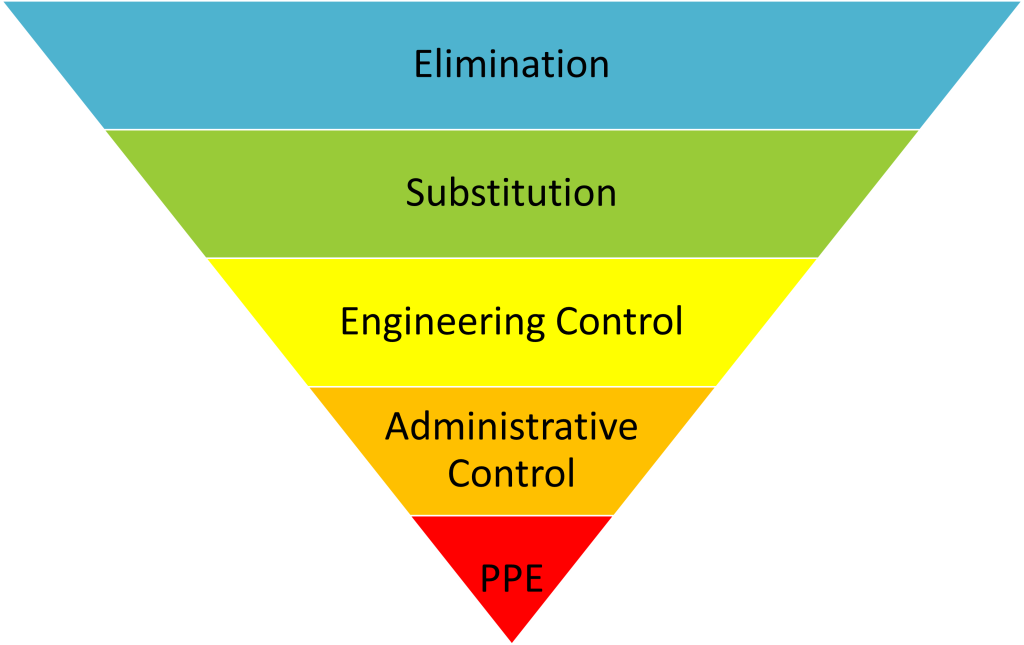
GENERAL HIERARCHY OF CONTROL
Elimination
Removal of the hazard in total from the working environment where possible. (But this is not always practical)
Reducing the hazard to an acceptable level by substituting something less hazardous/ reducing the amount of hazardous material used/ reducing the amount of exposure to it.
Substitution
Change work methods/patterns
Use of mechanical aids: robots, transporting or lifting equipment
Keeping the number of people involved in the task to a minimum, rotating work to minimise the amount of time involved.
Engineering Control
Isolation/segregation
Enclose the hazard so there is no interface between people and the hazard.
Putting guards around dangerous parts, using equipment in only one place
Administration Control
Control the numbers at risk by systems of work
Only trained people do the job
Personal Protective Equipment / PPE
This is a low level control
The equipment/clothing must be suitable for the task involved and be to the required safety standard.
PPE/C only protects the wearer, and can bring additional hazards such as reduced visibility/ hearing
Can you identify the areas of risk
The main areas of risk for tractors and other machinery in agriculture are:
- Moving Parts
- High Pressure
- Sharp Edges
- Rotating Parts
- Electrical Parts
- Other Hazards
Likewise for


The 5 steps of Risk Control
- What are the hazards?
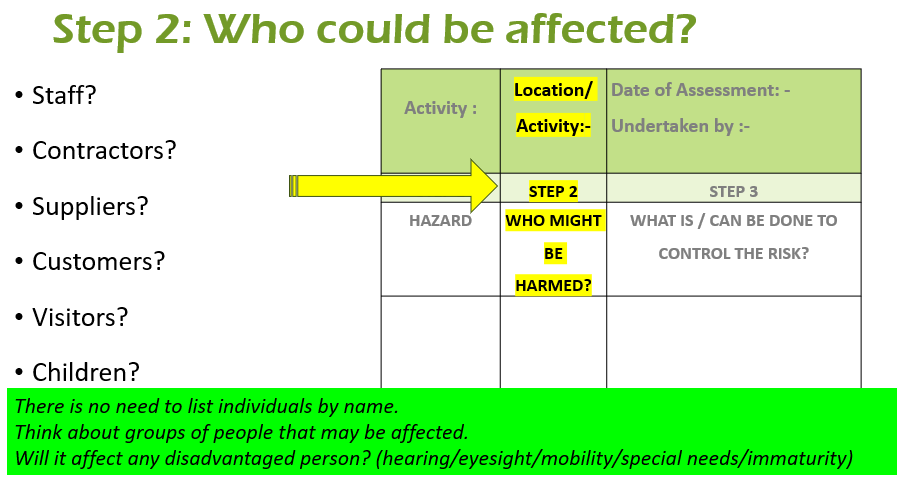
- Who could be affected?
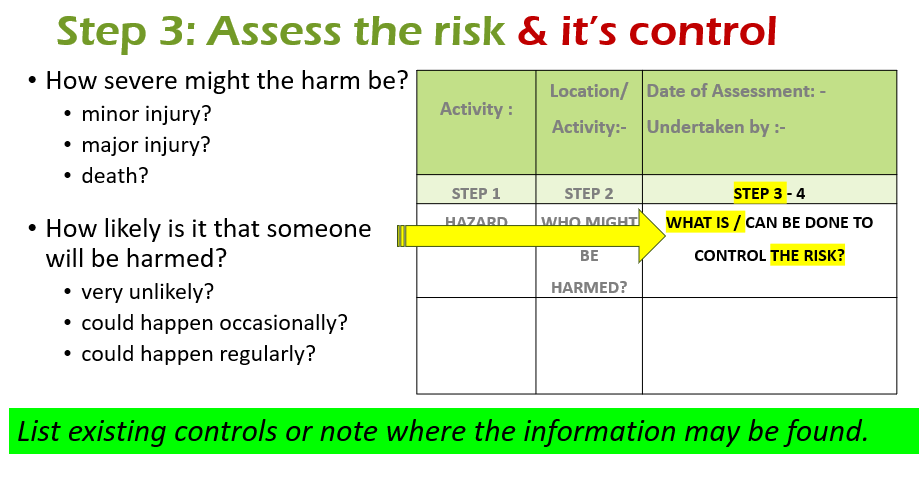
- Assess the risk
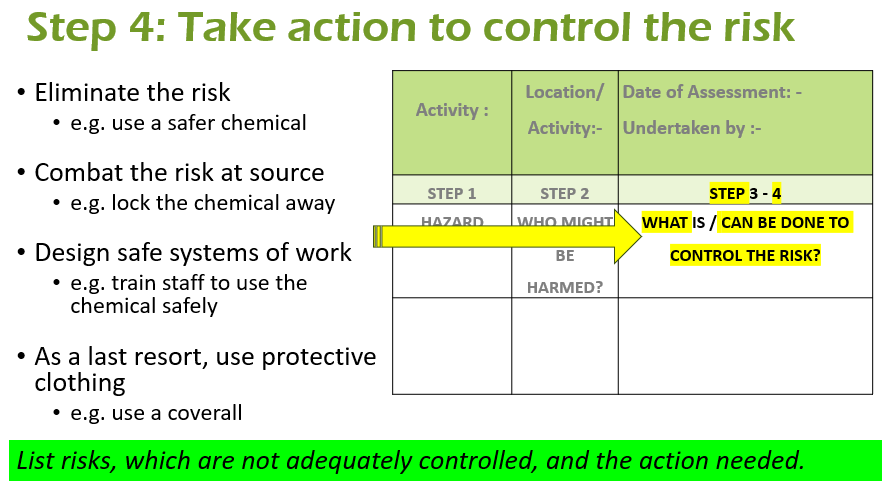
- Take action to control the risk
- Record and review your assessment
Step 1

Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Below is presentation which gives more details about “Health & Safety.”
Below is presentation which gives more details about “Risk Assessments and completing them.”
