Guide to Revising
Revision – funnel your knowledge…
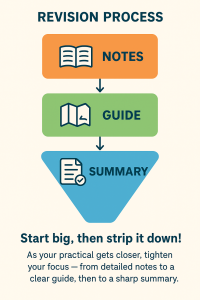
🧠 “Build your revision like a funnel — start wide with full notes, narrow it down to a clear guide, then finish with a short summary to keep the key points sharp for your practical.”
Revision process
🛠️ PREP STAGE – NOTES
Collect everything you need.
💡 BOOST STAGE – GUIDE
Streamline what matters.
🎯 LAUNCH STAGE – SUMMARY
Focus on the essentials for your practical.
In farming terms….
“Grow your knowledge, harvest your confidence!”
🌱 Notes – Sowing ideas
🌾 Guide – Growing understanding
🚜 Summary – Harvesting key points
Downloads
Livestock Technician Knowledge Revision Guide.
🐮Interactive revision for key livestock topics
— click to explore each section!
🐑 Livestock Units & Systems
Understand how different livestock systems operate and their efficiency, welfare, and environmental implications.
- Extensive systems: Grazing-based, lower input, more sustainable but slower production.
- Intensive systems: High input/output, efficient production but higher cost and environmental load.
- Examples: Indoor pig units, dairy parlours, free-range poultry, upland sheep grazing.
- Key considerations: Land type, climate, labour, market demand, and animal welfare.
🏠 Livestock Housing & Welfare
Animal housing affects comfort, welfare, productivity, and health.
- Provide dry, clean bedding (e.g., straw, sawdust) to prevent infections and improve comfort.
- Ventilation ensures fresh air and reduces disease spread.
- Maintain correct space allowances to prevent overcrowding.
- Check and clean water troughs regularly — access to fresh water is essential.
- Ensure housing allows for natural behaviours (e.g., perching for poultry, rooting for pigs).
🌾 Livestock Nutrition
Balanced nutrition ensures healthy growth, reproduction, and productivity.
- Ruminants require forage and concentrates — balance energy and protein.
- Monogastrics (pigs, poultry) need high-quality concentrates with essential amino acids.
- Water intake often exceeds feed intake — always ensure clean supply.
- Monitor Body Condition Score (BCS) to assess feeding effectiveness.
- Adjust rations for production stage (e.g., dry cow vs. lactating cow).
Mini Quiz: What’s the main difference between ruminant and monogastric digestion?
Hint: Think about fermentation and multiple stomach compartments!
🌱 Feedstuffs – Quality & Storage
Feed quality directly influences animal health and performance.
- Store feed in cool, dry areas to prevent mould and pests.
- Monitor dry matter (DM) content and nutrient value.
- Use FIFO (First In, First Out) to maintain freshness.
- Check silage for smell, pH, and colour — signs of spoilage reduce feed value.
- Keep records of delivery, batch number, and feed supplier for traceability.
🩺 Livestock Health
Health monitoring keeps livestock productive and reduces disease losses.
- Carry out daily health checks — look for changes in appetite, behaviour, or appearance.
- Follow vaccination and parasite control schedules.
- Maintain clean housing to prevent bacterial spread.
- Isolate and record sick animals promptly.
- Work with the vet to design a herd health plan.
🐄 Livestock Breeding
Effective breeding improves herd performance and efficiency.
- Use Estimated Breeding Values (EBVs) to select high-performing animals.
- Artificial Insemination (AI) allows selective and disease-safe breeding.
- Monitor heat signs in females and ensure timing of service is correct.
- Manage genetics to avoid inbreeding and improve resilience.
🌿 Grass & Forage
Grass management underpins livestock systems.
- Rotate grazing to prevent overgrazing and maintain sward quality.
- Monitor grass growth rates and adjust stocking accordingly.
- Conserve surplus as hay or silage for winter feeding.
- Test soil pH and nutrients — lime if needed to optimise growth.
- Multi-species swards (clover, herbs, grasses) can improve resilience and biodiversity.
⚠️ Health & Safety
Essential to protect everyone on the farm.
- Always wear PPE such as boots, gloves, and high-vis clothing.
- Follow safe systems of work when handling livestock or machinery.
- Keep yards clean and well-lit to reduce slip and trip hazards.
- Know your emergency procedures — first aid, fire exits, contact numbers.
- Regularly check and maintain tools and equipment.
📋 Risk Assessments
Helps identify and control workplace hazards.
- Identify hazards (livestock, machinery, chemicals, etc.).
- Assess risk levels — who could be harmed and how?
- Implement controls — PPE, training, signage.
- Review assessments regularly or after incidents.
🚜 Machinery & Tractors
Machinery must be used safely and efficiently on farm.
- Horsepower (HP): Choose machinery with suitable power for the job — too little = strain, too much = inefficiency.
- Tractor workings: Understand power take-off (PTO), hydraulics, and weight distribution.
- Attachments: Use appropriate implements for tasks — loaders, mowers, balers, trailers.
- Check tyre pressure, lighting, and brakes before use.
- Working conditions: Avoid fatigue and maintain clear visibility.
- Machinery legislation: Ensure LOLER and PUWER compliance, operator training, and safe maintenance logs.
🧫 Biosecurity
Prevents the introduction and spread of disease.
- Clean and disinfect vehicles, clothing, and equipment between farms.
- Control farm access — use visitor logs and disinfectant mats.
- Quarantine new or returning livestock.
- Keep wildlife and pests under control.
💷 Enterprise Performance & KPIs
Measures efficiency, productivity, and profitability of enterprises.
- Gross Margin: Output minus variable costs — key profitability measure.
- Physical performance indicators: Growth rates, calving intervals, mortality rates.
- Use data from farm records to identify trends and areas for improvement.
- Compare against industry benchmarks to assess performance.
- Implement SMART targets for continuous improvement.
