Guide to Revising
Revision – funnel your knowledge…
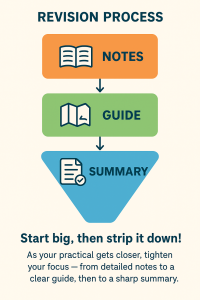
🧠 “Build your revision like a funnel — start wide with full notes, narrow it down to a clear guide, then finish with a short summary to keep the key points sharp for your practical.”
Revision process
🛠️ PREP STAGE – NOTES
Collect everything you need.
💡 BOOST STAGE – GUIDE
Streamline what matters.
🎯 LAUNCH STAGE – SUMMARY
Focus on the essentials for your practical.
In farming terms….
“Grow your knowledge, harvest your confidence!”
🌱 Notes – Sowing ideas
🌾 Guide – Growing understanding
🚜 Summary – Harvesting key points
Downloads
Crop Technician Knowledge Revision Guide.
🌱 UK Crops
Main Crop Groups
The UK grows a diverse mix of cereals, root crops, pulses and vegetables. Apprentices should know key growth stages, soil requirements, major pests and diseases, and harvest indicators.
- Cereals: wheat, barley, oats — focus on disease control, drilling windows, nitrogen timing.
- Oilseeds: mostly OSR — flea beetle risk, establishment challenges.
- Potatoes: blight management, irrigation, soil preparation.
Quick Check
- Which crop is most vulnerable to cabbage stem flea beetle?
- What are the three main cereals grown in the UK?
- Why are pulses important for soil fertility?
- Oilseed Rape (OSR)
- Wheat, Barley, Oats
- They fix nitrogen and improve soil fertility
🌿 Agronomy
What Agronomy Covers
- Crop Growth Factors: light, water, nutrients, temperature.
- Stress Diagnosis: nutrient deficiency spotting, pest/disease symptoms.
- Field Walking: thresholds, identification skills, using crop monitoring tools.
Quick Check
- Name two abiotic stresses and two biotic stresses.
- What is a treatment threshold?
- Why is field walking essential for crop health?
- Abiotic: drought, frost; Biotic: aphids, fungal diseases
- The point where pest/disease requires action
- To detect issues early and guide management decisions
🌾 Crop Nutrition
- Plant Nutrition: N, P, K, Mg, S plus micros like Mn, Cu, B.
- RB209: guidelines for fertiliser planning.
- Fertiliser Types: straight, compound, organic, controlled release.
- Liming: correcting low pH to maximise nutrient uptake.
Quick Check
- What nutrient is most commonly deficient on high pH soils?
- How does soil pH affect nutrient availability?
- What does RB209 help farmers decide?
- Iron (Fe)
- High pH can lock up nutrients making them unavailable
- Fertiliser type and application rates
🧱 Soil
- Soil Basics: texture, structure, organic matter, biota.
- Soil Survey: assessing type, pH, nutrient levels, maps.
Quick Check
- What is the ideal pH for most arable crops?
- Why is organic matter important?
- How does compaction affect yield?
- 6–7
- Improves structure, nutrient retention, water holding
- Reduces root growth and drainage, lowering yield
🚜 Crop Husbandry
- ICM: biological, cultural and chemical tools combined.
- Rotations: break pest cycles, manage weeds, improve soil.
- Growth Stages: GS30/31 for N timing, GS39 flag leaf protection.
- Varieties: disease ratings, maturity, yield potential.
- Chemical Control: safe use, labels, application timing.
Quick Check
- Why is GS39 a key timing for fungicides?
- Name one benefit of long rotations.
- What factors affect variety choice?
- Protects flag leaf for maximum yield
- Reduces disease and weed pressure
- Disease resistance, maturity, soil type, market demand
⚠️ Health & Safety
- Machinery competence and safe stop procedures.
- Tractor attachments and safe hitching.
- Risk assessments for field tasks.
- Biosecurity to prevent spread of pests & disease.
- Understanding legal responsibilities.
Quick Check
- What is the Safe Stop procedure?
- Name two key biosecurity actions.
- Why are guards essential on PTO shafts?
- Turn off engine, lower implements, disengage PTO, apply brakes
- Clean equipment, restrict visitor access
- Prevent entanglement injuries
📊 Enterprise Performance & KPIs
- Gross Margin: output minus variable costs.
- KPIs: yield/ha, cost per tonne, nitrogen use efficiency, labour hours.
- Benchmarking: comparing performance to industry standards.
Quick Check
- What is included in variable costs?
- How is gross margin calculated?
- Why is benchmarking useful?
- Seed, fertiliser, sprays, fuel, labour
- Gross Margin = Output – Variable Costs
- To compare performance and identify improvements
